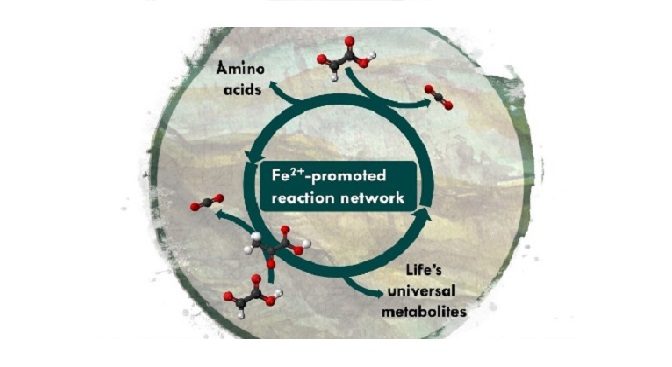
Synthesis and breakdown of universal metabolic precursors promoted by ironResearchers in Strasbourg, France, have found that mixing two small biomolecules, glyoxylate and pyruvate, in iron-salt-rich water produces a reaction network resembling life’s core biochemistry. This discovery provides insight into how chemistry on the early Earth primed the evolution of the most ancient … Continue Reading ››
Category Archives: Publications
Mirrors change chemical selectivity
A chemical reaction transforms the molecules that make up matter. To influence chemical reactions, chemists typically act on the molecules themselves, rather than the space in which the reaction takes places. However, researchers at the University of Strasbourg have shown that chemical reactions can indeed be influenced simply by conducting them between two appropriately spaced mirrors, kept only micrometers … Continue Reading ››
Enlightening full-color displays
Researchers from the University of Strasbourg & CNRS (France), in collaboration with University College London (United Kingdom), and Humboldt University Berlin (Germany), have shown that a subtle combination of light-emitting semiconducting polymers and small photoswitchable molecules can be used to fabricate light-emitting organic transistors operating under optical remote control, paving the way to the next … Continue Reading ››
The art of pastry: a graphene mille-feuille for highly sensitive health monitoring
Researchers from the University of Strasbourg & CNRS (France), in collaboration with Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznań (Poland) and the University of Florence (Italy), have developed a new generation of pressure sensors based on graphene and molecular “springs”. Thanks to their highest sensitivity, these devices are ideally suited for health monitoring and point-of-care … Continue Reading ››
Oscillating artificial microtubules
Oscillating artificial microtubules
Chemically fuelled processes control size oscillations of natural fibres inside the body such as microtubules or actin filaments. Researchers from the University of Strasbourg have now discovered similar size oscillations in a completely artificial system. Brightly coloured molecules form extended supramolecular fibres that can be controlled by redox chemistry. In a … Continue Reading ››
Direct photolithography on molecular crystals for high performance organic optoelectronic devices
{{unknown}}
CO2 coupling on iron parallels ancient biological pathway
Researchers at the University of Strasbourg have discovered a striking similarity between the way carbon dioxide (CO2) reacts with metals and the way that ancient microbes use CO2 to build their biomass, providing potential insight into how chemistry on the early Earth foreshadowed biochemistry in the first organisms.
The study was funded by the European Research … Continue Reading ››
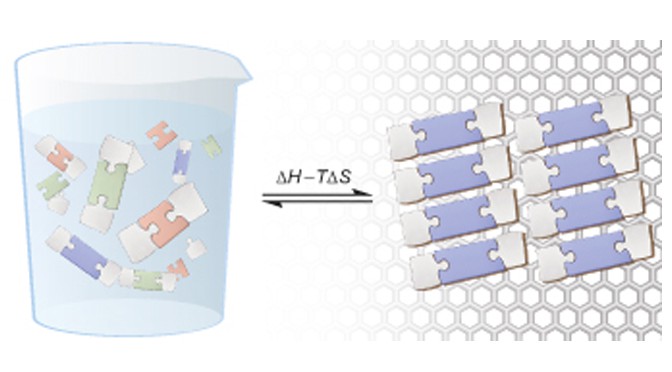
Dynamic covalent chemistry visualized!
A collaboration between two ISIS research groups (Lehn, Samori) has revealed dynamic covalent chemistry on surfaces. They state: "The results above taken together stress the crucial role of interactions with the surface as the selection force that drives the outcome of covalent chemical reactions, allowing or inhibiting given transformations and thus leads to … Continue Reading ››
Graphene–organic composites for electronics: optical and electronic interactions in vacuum, liquids and thin solid films
DOI: 10.1039/C3TC32153C (Feature Article) J. Mater. Chem. C,2014, 2, 3129-3143
Graphene exhibits exceptional mechanical, optical and electrical properties that are unfortunately accompanied by poor processability and tunability of its properties. The controlled interaction of graphene with tailor-made organic semiconductors (OSs) can offer a solution to solve these two … Continue Reading ››
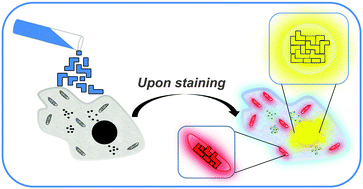
When self-assembly meets biology: luminescent platinum complexes for imaging applications
DOI: 10.1039/C3CS60453E (Review Article) Chem. Soc. Rev.,2014, Advance Article
Matteo Mauro *ab, Alessandro Aliprandi a, Dedy Septiadi a, Nermin Seda Kehr a and Luisa De Cola *a
Luminescent platinum complexes have attractive chemical and photophysical properties such as high stability, emission in the visible region, high emission quantum yields and long excited state lifetimes. … Continue Reading ››